The Benefits and Applications of Off-Grid Solar Systems
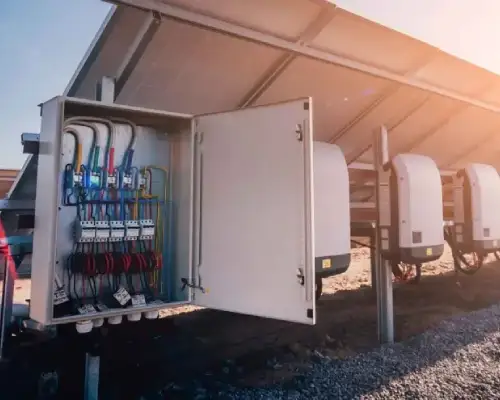

Off-Grid Solar Systems are revolutionizing energy access, particularly in remote areas with limited or no connection to traditional electricity grids. These systems provide an independent and reliable power source, enabling homes, businesses, and agricultural operations to harness solar energy efficiently. This article delves into the design, components, advantages, and diverse applications of Off-Grid Solar Systems.
What are Off-Grid Solar Systems?
-
Off-Grid Solar Systems operate independently of the central electricity grid. They rely on solar panels to generate electricity, which is then stored in batteries for use during the night or cloudy days. This independence makes them an ideal solution for rural and underserved areas.
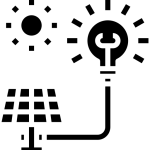
Key components of an Off-Grid Solar System include:
- Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Battery Bank: Stores energy for use when sunlight is unavailable.
- Inverter: Converts direct current (DC) from the panels into alternating current (AC) for use in appliances.
- Charge Controller: Regulates the flow of electricity to the batteries, preventing overcharging or deep discharge.
- Cables and Connectors: Ensure safe and efficient transmission of power.
These systems are designed to operate autonomously, providing a dependable source of energy even in the absence of a grid connection.
Advantages of Off-Grid Solar Systems
- Energy Independence: Off-Grid systems eliminate reliance on electricity grids, ensuring continuous power supply.
- Sustainability: They use renewable energy, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering carbon footprints.
- Cost Savings: While the initial investment may be high, these systems reduce or eliminate ongoing electricity costs.
- Adaptability: They can be customized to meet specific energy needs, from powering homes to running agricultural equipment.
- Reliability in Remote Areas: Ideal for locations where grid extension is expensive or impractical.
Applications of Off-Grid Solar Systems
- Residential Use: Remote homes and private farms benefit from reliable energy for lighting, appliances, and basic utilities.
- Agriculture: Farmers can use solar power for irrigation pumps, lighting, and small equipment, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- Businesses: Small workshops, shops, and offices in off-grid locations can maintain operations with a steady power supply.
- Community Projects: Schools, clinics, and community centers in remote areas can access reliable electricity for essential services.
Challenges and Solutions
Off-Grid systems face certain challenges:
- High Initial Costs: Advanced battery technology and installation can be expensive. However, subsidies and government incentives often offset these costs.
- Energy Storage Limitations: Batteries have finite storage capacities, requiring careful energy management. Emerging technologies, like lithium-ion batteries, are improving storage efficiency.
Conclusion
Off-Grid Solar Systems are more than a technological solution; they are a transformative tool for empowering remote communities and promoting sustainability. By offering energy independence and reducing environmental impact, these systems pave the way for a brighter and more inclusive future.